Disabling Windows components. How to enable or disable Windows components Which Windows 10 components should be enabled
All users should know what needs to be disabled in Windows 10 to make work even easier and safer. In fact, a person working with Windows must customize the OS for himself. Let's take a closer look at those services that need to be disabled to make using your computer more comfortable.
At the moment, the Windows operating system is considered the most popular among computer users. The latest version of the OS is Windows 10, it is more practical and adaptive than the previous version.
What to do first
Try more effective tools before you start disabling services that have little or no impact on performance.
- Download and run the world-famous Carambis Cleaner (download from the official website) - this is a program that will clean your computer of unnecessary garbage, as a result of which the system will work faster after the first reboot;
- Update all drivers in the system using the Driver Updater program (download via direct link) - it will scan your computer and update all drivers to the latest version in 5 minutes;
Both programs are developed by official Microsoft partners!
In the modern computer world, there are many different viruses. They can also be found in downloaded files and on potentially dangerous sites. At the moment, there are Antivirus programs that can warn about dangerous files and sites, as well as find and remove viruses on your computer.
Therefore, think carefully about whether you need to disable Windows 10 Defender? After all, without the participation of an antivirus, the device will quickly become filled with various virus files that can cause a system crash. If you still decide to disable it, we recommend a third-party manufacturer. Therefore, it is not recommended to disable security programs, but rather install one and constantly scan your PC for malicious files.
What services need to be disabled in Windows 10
In order to identify all active programs, you need to simultaneously press the buttons " Win" And " R" This combination brings up a command line in which you will need to enter “ services.msc».
Next, a list of all services that are on the device should appear on the screen. Stopping or disabling a service is done by double clicking the mouse. After disabling services, be sure to click “ Apply", otherwise the changes will not be saved.
Let's see which services need to be disabled in Windows 10:
- Dmwappushservice. Needed for routing WAP push messages. Telemetry function can be disabled if desired.
- Machine Debug Manager. Used by professional programmers. If you are not a programmer, disable it.
- NVIDIA Stereoscopic 3D Driver Service. The NVIDIA video card service can be disabled if you do not use 3D stereo images.
- NVIDIA Streamer Service. Harnesses the power of GeForce® GTX™ graphics cards to bring games from your PC to your SHIELD device. It is advisable to disable it if you do not use SHIELD technology and do not play PC games on the TV screen.
- NVIDIA Streamer Network Service.
- Superfetch. Disable it if you are using an SSD drive.
- Windows Search. Responsible for the search built into the system. Those. helps to find files in the system by name. If you don't use search, turn it off.
- Windows Biometric Service. Collection, processing and storage of biometric data.
- Firewall. If you are using and not the Windows Firewall, then disable it.
- Computer browser. Maintains a list of computers on the network and provides it to programs upon request. Irrelevant if you work with only one PC on the network.
- Wireless setup. If you access the Internet by connecting a cable rather than Wi-Fi, then this service is no longer necessary.
- Secondary login u. Responsible for logging into Windows from multiple accounts. If you have one account, you can disable it.
- Print Manager. Responsible for printing files using a printer. If it is absent, it is advisable to disable it.
- CNG key insulation.
- Internet Connection Sharing (ICS). If you do not share Internet access through this PC, for example, do not distribute Wi-Fi to other devices through it.
- Work folders. This service syncs files with a Work Folders server so they can be used on any device that has Work Folders configured. Disable it if you work with one PC or synchronization is not needed.
- Server. If you do not use the file and printer sharing features, you can disable it.
- Xbox Live online service.
- Geographic location service. Tracks system location and manages geofences for application interaction.
- Sensor data service.
- Sensor service.
- CD burning service. The time of CDs is fading into oblivion, so if there is no drive or there is a need to write information to a CD, we disable the service.
- Client License Service (ClipSVC). Disable it if you do not use applications from the Windows Store.
- Image download service. Responsible for loading images from the scanner and camera. If you don't have a scanner, you can also disable it.
- AllJoyn router service. Redirects AllJoyn messages to local AllJoyn clients. This is a popular protocol for the interaction of applications, devices and users over WiFi and Bluetooth (and other types of networks), regardless of the type of device. Don't use it? Turn it off.
- Data Exchange Service (Hyper-V). The mechanism for exchanging data between the virtual machine and the PC OS. Not relevant if you are not using a Hyper-V virtual machine .
- Guest shutdown service (Hyper-V).
- Heart Rate Service (Hyper-V).
- Hyper-V Virtual Machine Session Service.
- Hyper-V Time Synchronization Service.
- Data Exchange Service (Hyper-V).
- Hyper-V Remote Desktop Virtualization Service.
- Sensor monitoring service. Monitoring various sensors.
- Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service. Provides dispatching of incoming messages addressed to the application service. By default the service is disabled. If you are optimizing your home computer, make sure that the services are disabled.
- Portable Device Enumerator Service. Provides the ability to synchronize and automatically play files from portable devices. This service is also of little use and can be disabled.
- Bluetooth support service. Disable it if you don't use Bluetooth.
- Program Compatibility Assistant Service.
- Windows Error Logging Service.
- BitLocker Drive Encryption Service. If you don't use disk encryption, disable it.
- Services that are started when installing various programs. You should pay attention to the services that appear when installing various programs. You won't need many of these services either.
- Remote registry. Allows remote users to change registry settings on this computer.
- Application identity.
- Fax machine. Allows you to receive and send faxes using the resources of this computer and network resources.
- Connected user functionality and telemetry. Applies to telemetry - disable if desired.
All of the above services can be disabled at the user’s request, because they only slow down the device’s performance.
Should I disable Windows 10 updates?
For any device, updates are very important. They help improve programs, making them more advanced and functional. But it often happens, especially on older computer models, that after updates the device begins to show poor performance, constantly freeze and consume more traffic.
And here many people have a question: is it necessary to disable Windows 10 updates? Of course, this is not recommended, because without updates, the computer will quickly become outdated and will not be able to perform some functions. But for those users who are severely limited in traffic, they can disable updates.
A firewall is a modern method of protecting information data on a computer. But if you are wondering, should you disable the firewall on windows 10? It is strictly not recommended to do this in all cases.
Only if the user has a similar replacement method for protecting information data, then it is possible to disable it.
To disable it, just go to the “Control Panel” on your computer and select the appropriate item. After disabling, do not forget to click the “Apply” button to save all changes.
Windows 10 has many additional features that you can enable or disable through the Control Panel. Some of them are intended for servers and corporate networks, while some are useful for the average user. In today's article, we'll look at what each function means and how to enable or disable it.
These components take up space on your hard drive even when disabled. But don’t rush to enable them all; perhaps some of them will reduce system performance or cause security problems.
How to view additional components and how to enable or disable them.
In Windows 10, some settings have been moved from the Control Panel to Settings, and some are only available through the panel.
1. Open "Programs and Features": one of the ways is in the search bar or in the "Run" menu (run by pressing the Win+R keys) write appwiz.cp l and press Enter.

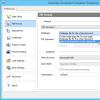
2. On the left side, open Turn Windows features on or off.

The "Windows Components" window will open in front of you. You can also launch this window by entering in the search bar or in the menu execute optional features

In Windows components, you will see the available functions, those with a checkmark are enabled, and those without a checkmark are disabled. If there is a square with a plus in front of a component, then it contains additional parameters, and you can enable both the entire component and part of its functions. Click on the plus to see a list of additional component parameters. To install a component, you need to check the box in front of it and click "OK", to remove the component - uncheck it and click "OK".
Additional Windows 10 features
What to turn on and what to turn off from this list? Windows 10 Pro and Home have a different set of components; in today's article we will look at the more complete set provided in the professional version of Windows 10:
.NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0): This component is needed to run applications written in these versions of .NET. Windows will automatically install this component if the application requires it;
.NET Framework 4.6 Advanced Services: also a necessary component for running applications. And also this component will be automatically installed as needed;
Hyper-V: Microsoft virtualization tool. It contains the main platform and tools for managing and using virtual machines;
Internet Explorer 11: if you don’t need the outdated Internet Explorer browser, you can disable it completely;
SNMP protocol: an old protocol for managing routers, switches and other network devices. Useful for people who are still working in an environment using this old protocol;
Windows Identity Foundation 3.5: older NET applications may still use this component. If some old application requires this component from you, check the box and install it;
Windows PowerShell 2.0: more advanced command line. It is enabled by default, but if you do not use it you can disable it. For example, with its help you can;

Embedded IIS Web Engine: ordinary users do not need this component. Used by software developers and IT specialists;
Built-in shell launcher: a new feature in Windows 10 that allows applications to run in a secure isolated space if they are programmed to do so. The average user does not need this component;
Telnet client: Telnet commands allow you to remotely connect to the command line interface on computers and devices running a Telnet server. Telnet is not secure, so it is recommended to enable it if you really need it;
TFTP client: allows you to transfer files using the TFTP protocol. This protocol is outdated and insecure; it may be useful on older devices. But it is unnecessary for most users;
Work Folders Client: this component allows you to synchronize folders from the corporate network to your computer;
Components for working with multimedia: if you do not use Windows Media to play video and audio, here you can disable it;
Legacy components: Previously, this component was part of DirectX, and was used to create networks and multiplayer games. Windows 10 will automatically install this component if some old game requests it during installation;
Manager Administration PackRAS connections: This tool allows you to create custom remote access profiles for VPN. Used by IT specialists mainly in corporate networks;
Printing to PDF: adds the ability, you can also use it. By default it is enabled, but if for some reason you do not need it, uncheck it and click “OK”;
API support for remote differential compression: algorithm for comparing synchronized files. Sometimes installed applications require this function, although there are not many such applications;
SMB 1.0/CIFS file sharing support: Allows file and printer sharing with older Windows (4.0 to XP). Linux and Mac operating systems can also use the older SMB protocol to share files and printers;
RIP Listener: This service is only useful if you have a router that supports RIPv1. This may be useful on a corporate network, but will not be useful at home;
Simple TCPIP services: This is a set of additional network services to troubleshoot some corporate network problems. But it is unlikely to be useful to the average user;
Microsoft Message Queuing Server: This is an old service for sending messages over untrusted networks. If the connection is lost, the messages are stored in a buffer and sent immediately after it is restored. This feature is needed by some enterprise applications;
Windows Activation Service: This feature is only useful to software developers. This component is associated with Internet Information Services (IIS);
Active Directory Services for lightweight directory access: provides an LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) server. It runs as a Windows service and provides a directory for authenticating users on the network. This is a lightweight alternative to a full Active Directory server, and will only be useful on some corporate networks;
Internet Information Services: provides web and FTP IIS servers from Microsoft along with tools for server management;
XPS Services: Allows you to print XPS documents. Microsoft created this document format in Windows Vista, although printing to PDF is already a better option. Here you can disable printing in XPS, thereby deleting this printer. Although you can go into printers and use the right-click menu to delete a given printer;
Document printing services: Internet and Windows print client, fax and scanning functions are enabled by default. They allow you to print over the network, send faxes and scan. You can also add support for the LPD and LPR network printing protocols, although these are older and not often needed, only if you have a connection to a network printer that requires them;
MultiPoint Connector: Allows your computer to be monitored and controlled using MultiPoint Manager and the application bar. This is only useful on corporate networks, and only if those networks use these management tools;
XPS Viewer: the application allows you to view XPS documents;
Windows TIFF IFilter: The feature allows Windows Indexing Services to parse .TIFF files and perform optical character recognition (OCR). It is disabled by default as it is an intensive process and creates a load. But, if you use a lot of TIFF files—for example, if you regularly scan paper documents into TIFF—this can be a useful feature that allows you to search for those scanned documents more easily.
Most users won't need the Windows Features window, because Windows 10 will install everything you need automatically when needed. But still, you may need to add something yourself or disable it. We can talk more extensively about these functions, but is it worth it? If you have any additions, write comments! Good luck to you :)
Some features and programs included in Windows 10 are disabled by default, but you can start them manually. Using the same methods, you can deactivate many system services and applications. The component management menu is located in the system settings.
What should not be disabled
Firstly, it is worth considering that disabled components are not erased from the system and remain in the hard drive memory. They are temporarily unavailable, meaning they cannot be found or launched until the user reactivates them in Windows settings. The only reason to block access to some programs is to protect inexperienced users from accidentally using them with unpleasant consequences.
Secondly, the system depends on some components, so disabling them may cause Windows to start working incorrectly or stop responding altogether. If you do not know what a particular service is needed for and whether it can be deactivated, then do not touch this component. Otherwise, there is an increased risk that you will have to spend a lot of time restoring the system. For example, disabling the PDF Print service will prevent Windows from working with PDF files, and if the NET Framework is disabled, many applications will not be able to open.
Activating and deactivating components
There are several ways to view the list of enabled and disabled components and edit it. There is no need for third-party programs, since all the necessary tools are built into Windows 10. At the end of the article there is a table listing all the components and the tasks they perform. Using it, you can understand which components you need enabled and which ones you don’t.
Via control panel
The control panel is the main application of the system, which contains almost all the settings that the user will ever have to contact. It also contains component parameters:
- Expand the control panel by searching for it using the system search bar. Opening the control panel
- Go to the "Programs and Features" block. It can be found by name using the search bar.
 Open the “Programs and Features” section
Open the “Programs and Features” section - Click on the line “Turn Windows features on or off.” Please note that accessing this section requires administrator rights.
 Click on the line “Turn Windows components on or off”
Click on the line “Turn Windows components on or off” - A complete list of components will unfold: those that are enabled have a dark square, those that are disabled have a white, unfilled square. If a component has a plus icon, then it has subcomponents, the list of which opens by clicking on the plus icon. Disabling a main component will deactivate all its subcomponents.
 We choose which components should be enabled and which should be disabled
We choose which components should be enabled and which should be disabled
Through system parameters
An alternative way to configure the system is to use the Settings application. Using it you can also perform detailed configuration of many Windows characteristics, including components:
- Expand the “Settings” application; you can find it by name using the system search bar.
 Open system parameters
Open system parameters - Go to the "Applications" block.
 Click on the “Applications” section
Click on the “Applications” section - While in the “Applications and Features” sub-item, click on the “Manage additional components” line.
 Click on the “Manage additional components” button
Click on the “Manage additional components” button - A list of used components appears. To disable one of them, left-click on it, and then click the “Delete” button.
 Click the “Delete” button
Click the “Delete” button - To add a new component, use the “Add component” button, after clicking which a list of unused services will open. Select the one you need and click on the “Install” button.
 Click the “Install” button
Click the “Install” button
Video: Setting up Windows 10 components
Table: list of components and their tasks
Using the table below you can find out what a particular component is needed for. With this information, you can decide for yourself which components should be disabled and which should be left enabled.
| Component name | Component task |
| NET Framework 3.5 | necessary for running programs written in .NET. |
| .NET Framework 4.6 Advanced Services | also used by programs written in .NET |
| Hyper-V | required for virtual machines to work |
| Internet Explorer 11 | the standard browser used in all previous versions of Windows. Edge replaced in Windows 10 |
| SNMP protocol | network device management protocol |
| Windows Identity Foundation 3.5 | used by older programs written in .NET |
| Windows PowerShell 2.0 | a modern command line that largely copies the standard one, but also complements it |
| Embedded IIS Web Engine | software developer tool |
| Built-in shell launcher | Allowing applications to run in a secure isolated space if they are programmed to do so |
| Telnet client | Telnet commands allow you to connect remotely to a command line interface |
| TFTP client | transfer files via TFTP |
| Work Folder Client | this component allows you to synchronize folders from the corporate network to your computer |
| Components for working with multimedia | if you do not use Windows Media to play video and audio - here you can disable it |
| RAS Connection Manager Administration Pack | This tool allows you to create custom remote access profiles for VPN. Used by IT specialists mainly in corporate networks |
| Print to PDF | responsible for viewing, editing, working and printing files in the PDF extension |
| Support for API remote differential compression | algorithm for comparing synchronized files |
| SMB 1.0/CIFS file sharing support | allows file and printer sharing with older Windows (4.0 to XP) |
| RIP Listener | This service is only useful if you have a router that supports RIPv1 |
| Simple TCPIP Services | this is a set of additional network services to troubleshoot some corporate network problems |
| Microsoft Message Queuing Server | This is an old service for sending messages over unreliable networks. If the connection is lost, the messages are stored in a buffer and sent immediately after it is restored |
| Windows Activation Service | necessary for software developers and used by them. This component is associated with Internet Information Services (IIS) |
| Active Directory Services for Easy Directory Access | working with LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) servers |
| Internet Information Services | provides web and FTP IIS servers from Microsoft along with tools for server management |
| XPS Services | printing files in XPS extension |
| Document Printing Services | Internet and Windows print client |
| MultiPoint Connector | monitoring and control using MultiPoint Manager and application panel |
| XPS Viewer | viewing elements in XPS format - documents |
| Windows TIFF IFilter | analysis of .TIFF files and optical character recognition (OCR). |
By including new components, you can increase the capabilities of the system while disabling old ones - protecting inexperienced users from incorrect use of certain programs. But remember that you can only get rid of those services that are not involved in the operation of the system and the launch of applications.
Hello! We continue to disassemble the Windows 10 operating system! Today you will learn how to enable or disable components on a Windows 10 computer. To configure components, open the menu at the bottom of the screen on the left "Start". In the window that opens, in the list of all applications, at the bottom, open the tab "Windows Utilities". In the list that opens, click on the tab "Control Panel".



By default, you can enable or disable the following components:
- .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0)
- Internet Explorer 11
- SNMP protocol
- Windows Identity Foundation 3.5
- Windows PowerShell 2.0
- Embedded IIS web engine
— Telnet client
— TFTP client
— Work folder client
— Components for working with multimedia
— Legacy components
— Print to PDF (Microsoft)
— API support for remote differential compression
- Support for SMB 1.0/CIFS file sharing
— Windows Subsystem for Linux (beta)
— RIP Listener
- Simple TCPIP services (such as echo, daytime, etc.)
- Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ)
- Windows Activation Service
- Internet Information Services
- XPS Services
— Print and document services
- XPS Viewer
— Windows TIFF IFilter filter
The transition to the newer Windows 10 operating system has raised a lot of questions for many users. After all, the developers have significantly changed the control interface of this version of the OS compared to Windows 7. For example, it was hidden in an unknown place and can no longer be accessed in the usual way through the Start menu in Windows 10.
In this article we will tell you where “Programs and Features” are located in Windows 10 and how you can see the list of programs installed on your computer.
Manage installed programs in Windows 10
There are two ways to view the removal of all installed programs in Windows 10 - through the familiar “Programs and Features” control panel item, as well as through the global Windows settings.
How to find Programs and Features in Windows 10?
It is useless to look for them in the Start menu. But you can find it through a search. True, you first need to go to the “Control Panel” and then find “Programs and Features” in it.
To do this, click on the magnifying glass icon in the lower left corner of the screen just to the right of the Start menu. In the input field that opens, write “Control Panel”.
Opening the control panel
After that, in the search results we go to the first line.

Let's move on to programs and components
In the already familiar Control Panel, we find programs and components and open them. This will display a list of all installed programs on your computer that .
Updated Programs and Features - Apps and Features
In Windows 10, the developers decided to slightly update the window with installed programs. It is now called "Applications and Features" in Windows global settings.
To go to it, you need to click on the message icon in the lower right corner of the screen and select “All parameters” in the window that opens.

Opening Windows 10 settings
In the “Windows Settings” window, select “Applications”, after which the “Applications and Features” window will open, which, like in “Programs and Features”, displays a list of all installed programs with the ability to remove them.